

Understanding Current Transformer Measurement
Principles, Applications, and Products
Photovoltaic systems, heat pumps, and electric vehicle charging stations generate high currents that standard measuring devices can't handle. This is where current transformer measurement comes into play, offering a practical solution for accurate high-current measurement. In this article, we’ll explore what current transformer measurement is and the products in the Krannich portfolio designed for this purpose.
Table of Content
What is Current Transformer Measurement and How Does It Work?
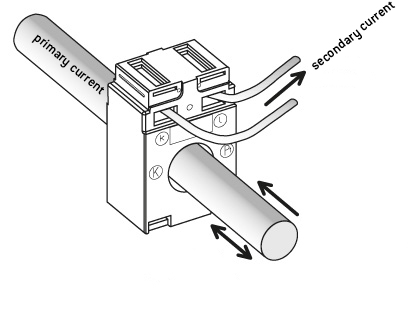
Current transformer measurement, often referred to as CT measurement, is a method used in electrical systems to indirectly measure high currents that standard measuring devices cannot handle. This technique employs current transformers (CT) and voltage transformers (VT) to reduce high currents and voltages to a measurable level.
An electrically charged line generates a magnetic field. In current transformers, this magnetic field induces a "secondary current," which is significantly smaller than the primary current. This reduction is determined by a fixed multiple, known as the transformation ratio. The measuring device captures this smaller secondary current and, using the transformation ratio, calculates the original primary current.
An example:
- consider a primary current of 200A with a transformation ratio of 40:1.
- The secondary current would be 200A/40=5A.
- If the smart meter measures 2A as the secondary current, then 2A×40=80A flows in the primary circuit.
This indirect measurement method allows for precise monitoring of high-current systems, ensuring safety and accuracy in various applications such as photovoltaic systems, heat pumps, and electric vehicle charging stations. The simplicity and reliability of current transformer measurement make it a widely used solution in managing electrical loads.
Why is current transformer measurement important?
Accurate measurement using suitable transformers is important for several reasons:
- Accurate billing: Inaccurate data can lead to inflated bills.
- Load management: With accurate measurement data, companies can analyze and optimize their load profile, helping to identify peak loads and take measures for load shifting or reduction.
- Monitoring and safety: Accurate monitoring of electrical loads can help detect potential issues such as overloads or malfunctions early on and take appropriate measures.
Current transformers in our portfolio
- ABB Stotz-Kontakt CM-CT 100/5A to 600/5A
- Enphase CT-100-Split-Row 100A
- Fronius CT V 100A to 400A
- Fronius Split-Core CT 100/5A to 400/5A
- Kaco CT für HY-Switch 100A
- Solar Edge SE-CTB-4x4-1200A to 3000A
- Solar-Log Pro 380-CT 100A to 500A
- Solar-Log Pro 380-CT
- Solar-Log Pro 380 CT 250A für Pro 380
- Sungrow CT for DTSU666-20 100A and 250A
In the designation of the CTs, it can be seen for which current strength the measuring transformer is approved at most. This value should not be exceeded, as otherwise the measurement results may become inaccurate.
Important questions about current transformer measurement
Who benefits from current transformer measurement?
Current transformer measurement is particularly useful for:
- Large industrial facilities: These require accurate measurements due to their high energy consumption.
- Commercial buildings: Office complexes, shopping centers, and similar facilities benefit from accurate data for cost control and energy efficiency.
- Energy suppliers: They use current transformer measurements to accurately capture and bill their customers' electricity consumption.
What types of current transformer meters are there?
There are three types of current transformer meters that can be used for current transformer measurement:
- Current Transformers (CT): These measure the current and convert it into a lower, measurable value.
- Voltage Transformers (VT): These measure voltage and convert it into a lower, measurable value.
- Combination Transformers: These devices combine both current and voltage measurements in one unit.
When do I need current transformer measurement?
Current transformer measurement is necessary when:
- The power consumption is so high that it exceeds the capacity of direct measuring meters (typically over 100 A).
- More accurate measurements are needed for load monitoring and control.
- Legal or contractual requirements mandate it.
What are the costs of current transformer measurement?
The costs for a current transformer measurement can vary widely based on several factors:
- Cost of transformers: Current and voltage transformers can vary in price depending on specifications and accuracy class. The price varies depending on the model, functionality, and compatibility, ranging from a mid double-digit to a mid triple-digit amount.
- Installation costs: Installation requires skilled personnel and can vary based on system complexity.
- Maintenance costs: Regular maintenance and calibration are necessary to ensure accuracy.
The total cost for a complete current transformer measurement setup and installation can amount to several thousand euros.
What measurement deviations are permissible in current transformer measurements?
Permissible measurement deviations in current transformer measurements are defined by standards and regulations. Typically:
- Current Transformers: Accuracy classes such as Class 0.2, 0.5, or 1.0 exist, with 0.2 being the most accurate.
- Voltage Transformers: Similar accuracy classes apply as with current transformers.
Accuracy depends on the class of the transformers and must meet application-specific requirements.
Which transformer meters can be used for transformer measurement?
Various types of meters can be used for current transformer measurements, including:
- Digital Meters: Modern digital meters that offer high accuracy and additional features such as data logging and remote reading.
- Analog Meters: Traditional analog meters that are increasingly being replaced by digital variants.
- Multifunction Meters: Devices that can measure and record multiple parameters (current, voltage, power).
- Current transformers that are integrated into other devices. This is the case with some inverters.
In conclusion, current transformer measurement is essential for accurately monitoring and managing high-current electrical systems. By choosing the right products and understanding their application, businesses can ensure precise billing, effective load management, and enhanced safety.